Preoperative Assessment and Preparation
A comprehensive preoperative assessment ensures patient safety by identifying risks and optimizing conditions. This includes evaluating medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to guide anesthetic planning.
Clear communication with surgeons and patients is crucial. Informed consent must be obtained, outlining anesthesia risks and benefits. A structured approach ensures a smooth surgical experience for all parties involved.
1.1 Patient Evaluation and Risk Stratification
Patient evaluation involves a thorough review of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to identify potential risks. This step ensures personalized anesthesia planning and minimizes complications during surgery.
Risk stratification categorizes patients based on their health status, guiding anesthesiologists in selecting appropriate techniques. Clear communication with the surgical team ensures aligned goals and optimal patient outcomes.
1.2 Selection of Anesthetic Technique
The choice of anesthetic technique depends on the patient’s health, surgical requirements, and potential risks. Regional anesthesia is often preferred for procedures involving extremities or the abdomen, while general anesthesia may be necessary for more complex surgeries.
Anesthesiologists tailor the approach to minimize complications, ensuring patient safety and comfort. Evidence-based guidelines and interdisciplinary collaboration guide the final decision, optimizing outcomes for each case.
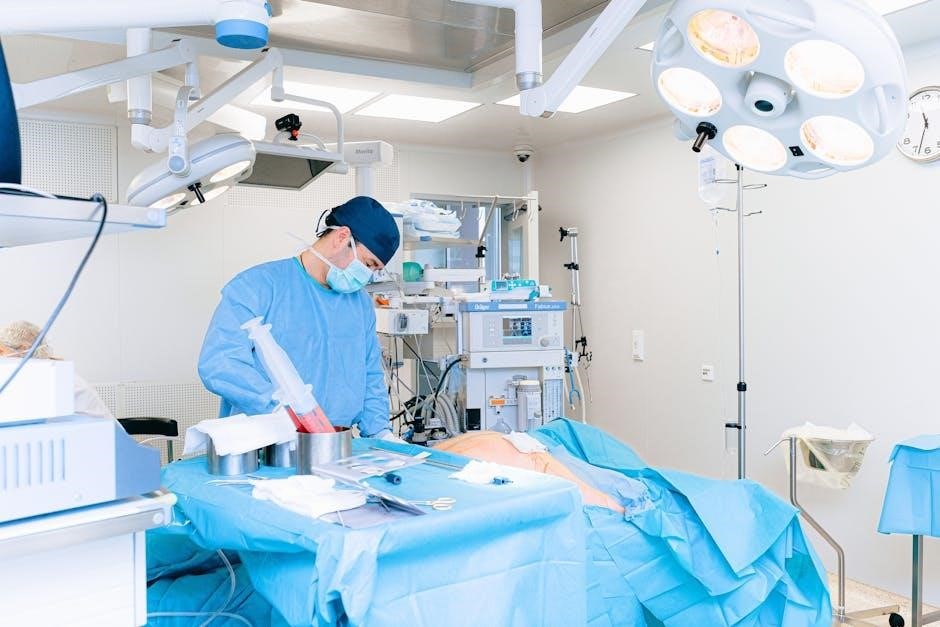
Intraoperative Anesthesia Management
Intraoperative management involves continuous monitoring and adjusting anesthesia levels to ensure patient stability and comfort. Advanced technologies and real-time data guide anesthesia delivery, optimizing surgical outcomes while minimizing risks.
Effective pain management and meticulous attention to physiological parameters are critical. Anesthesiologists must anticipate and respond to complications promptly, maintaining a safe and controlled environment throughout the procedure.
2.1 Monitoring and Maintenance of Anesthesia
Meticulous monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, is essential during anesthesia. Advanced equipment ensures continuous assessment of the patient’s physiological state, enabling swift adjustments to maintain stability.
Anesthesia depth is closely monitored to prevent awareness or excessive sedation. Regular checks of anesthetic drug delivery and equipment functionality are critical to ensure patient safety and optimal surgical conditions throughout the procedure.
2.2 Intraoperative Pain Management
Intraoperative pain management involves balancing analgesia with patient stability. Techniques include local anesthetics, regional blocks, and systemic opioids, tailored to surgical requirements.
- Epidural and spinal anesthesia provide effective regional pain relief, reducing systemic opioid needs.
- Titration of anesthetic depth and analgesic drugs ensures optimal pain control while maintaining hemodynamic stability.
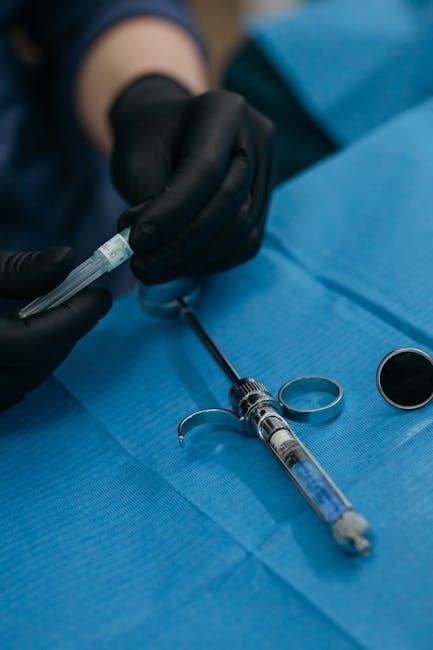
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care focuses on monitoring vital signs, managing pain, and preventing complications. Close observation in the PACU ensures a smooth recovery and addresses any immediate concerns promptly.
3.1 Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) Management
In the PACU, patients are closely monitored for recovery from anesthesia. Vital signs, oxygenation, and pain levels are assessed. Nurses and anesthesiologists collaborate to address complications promptly, ensuring patient safety and comfort during the transition to recovery.
3.2 Postoperative Pain Management Strategies
Effective postoperative pain management involves a multimodal approach, combining pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods. Anesthesiologists tailor strategies to individual needs, using analgesics and regional techniques. Regular monitoring ensures optimal pain relief while minimizing side effects. Clear communication with patients and surgical teams is essential to enhance recovery outcomes and patient satisfaction.
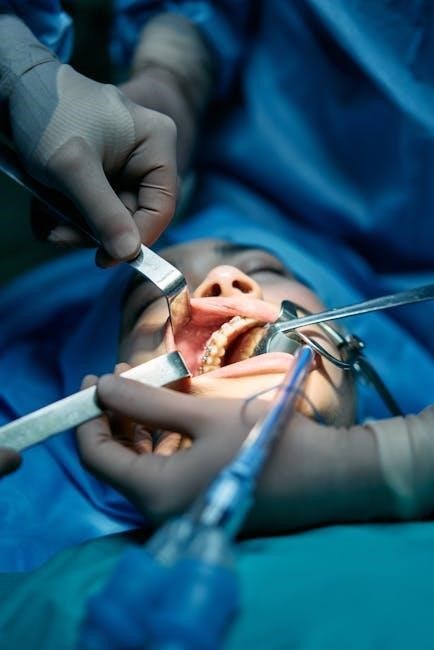
Special Considerations in Surgical Anesthesia
Special considerations include managing anesthesia for emergency procedures, ensuring rapid patient preparation, and optimizing regional anesthesia techniques to enhance safety and outcomes in high-stakes scenarios.
4.1 Anesthesia for Emergency Surgical Procedures
Anesthesia for emergency surgeries requires rapid patient assessment and preparation. Prioritizing airway management and hemodynamic stability is crucial. Communication with the surgical team ensures coordinated care. Minimizing delays while maintaining safety protocols is essential in these high-pressure situations.
4.2 Regional Anesthesia Techniques
Regional anesthesia involves numbing specific areas of the body, reducing pain during and after surgery. Techniques like epidural, spinal, and peripheral nerve blocks are commonly used. These methods minimize systemic side effects and promote faster recovery. Proper patient selection and anatomical knowledge are essential for safe and effective application. Advanced training and precision are required to ensure optimal outcomes and patient comfort.
Communication and Teamwork in the Operating Room
Effective communication and teamwork are crucial in the operating room. Anesthesiologists must collaborate closely with surgeons and nurses to ensure patient safety and efficient workflow. Clear communication strategies are essential for maintaining situational awareness and addressing emergencies promptly. The role of anesthesia nurses is vital in facilitating seamless teamwork and maintaining high standards of patient care.
5.1 Effective Communication Between Anesthesiologists and Surgeons
Effective communication between anesthesiologists and surgeons is critical for patient safety and successful outcomes. Clear and timely exchanges ensure seamless coordination during procedures, addressing anesthesia-related concerns promptly. Open dialogue fosters trust and collaboration, enhancing teamwork in high-stakes environments. Regular updates on anesthesia plans and patient status are essential. Preoperative briefings and debriefings further strengthen this collaboration, ensuring alignment on surgical goals and patient care strategies.
5.2 Role of Anesthesiologists in Surgical Team Dynamics
Anesthesiologists play a pivotal role in surgical team dynamics, ensuring patient safety and procedural efficiency. They coordinate with surgeons, nurses, and other specialists, providing expertise in anesthesia care. Beyond administering anesthesia, they monitor vital signs, manage emergencies, and contribute to decision-making. Their leadership enhances teamwork, fostering a collaborative environment. Effective communication and problem-solving skills are essential, as they anticipate and address surgical challenges, ensuring optimal patient outcomes and seamless workflow in the operating room.
Anesthesia-Related Guidelines and Protocols
Anesthesia guidelines and protocols establish standards for safe practice, ensuring compliance with evidence-based recommendations and regulatory requirements. They promote consistency and quality in patient care delivery.
6.1 Evidence-Based Guidelines for Anesthesia Practice
Evidence-based guidelines in anesthesia practice are systematically developed recommendations, integrating clinical research and expert consensus. They aim to optimize patient outcomes, reduce risks, and enhance procedure efficiency. These guidelines address preoperative assessment, intraoperative management, and postoperative care, ensuring adherence to best practices. Regular updates reflect advancements in research and technology, promoting safer and more effective anesthesia delivery across surgical settings.
6.2 Compliance with Safety Protocols in Anesthesia
Compliance with safety protocols in anesthesia is critical to minimize risks and ensure patient safety. These protocols include proper equipment checks, medication labeling, and standardized procedures for emergency situations. Adhering to guidelines like those from the American Society of Anesthesiologists ensures consistency and reduces complications. Continuous monitoring and regular training are essential to maintain high safety standards in anesthesia practice.
Advances and Future Trends in Anesthesia
The field of anesthesia is evolving rapidly, with emerging technologies like AI-driven monitoring systems and automated drug delivery improving precision. Non-invasive monitoring devices and pharmacogenomics enable personalized anesthesia plans. Additionally, alternative techniques such as clinical hypnosis are gaining traction, offering patients more options and enhancing recovery outcomes.
7.1 Emerging Technologies in Anesthesia Delivery
Emerging technologies in anesthesia include AI-driven systems for precise drug delivery and real-time monitoring. Automated anesthesia machines enhance safety by reducing human error. Pharmacogenomics enables personalized anesthesia plans based on genetic profiles. Non-invasive devices monitor vital signs without discomfort, improving patient care. These innovations aim to optimize anesthesia administration, ensuring tailored and efficient treatment for diverse surgical procedures.
7.2 Role of Clinical Hypnosis and Alternative Techniques
Clinical hypnosis is increasingly recognized for pain management and anxiety reduction. It enhances patient relaxation, reducing the need for pharmacological agents. Alternative methods like guided imagery and mindfulness improve recovery outcomes. These techniques complement traditional anesthesia, offering a holistic approach. Integration into anesthesia practice promotes patient-centered care, addressing both physical and psychological needs effectively during surgical procedures.
Complications and Crisis Management
Early recognition of anesthesia-related complications is critical. Effective crisis resource management ensures timely intervention, minimizing risks and optimizing patient outcomes during emergencies.
8.1 Recognition and Management of Anesthesia-Related Complications
Early recognition of anesthesia-related complications is crucial for patient safety. Vigilance in monitoring vital signs and clinical indicators ensures prompt identification of issues like respiratory depression or cardiac arrhythmias.
Effective management involves immediate intervention, such as adjusting ventilation or administering medications. A structured approach, including crisis resource management, enhances teamwork and decision-making, minimizing adverse outcomes and optimizing recovery.
8.2 Crisis Resource Management in Anesthesia
Crisis resource management (CRM) in anesthesia focuses on enhancing teamwork, communication, and decision-making during high-stress situations. It emphasizes leadership, task delegation, and maintaining situational awareness to ensure patient safety.
Regular training in CRM techniques prepares anesthesiologists to manage emergencies effectively, fostering a culture of safety and collaboration within the surgical team. This approach minimizes errors and improves outcomes during critical events.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Ethical practices in anesthesia prioritize patient autonomy, confidentiality, and informed consent. Anesthesiologists must adhere to professional standards, ensuring decisions align with legal and moral frameworks.
Legal implications include liability for negligence and the duty to document procedures accurately. Compliance with regulations safeguards both patients and practitioners, upholding trust and accountability in care delivery.
9.1 Informed Consent and Patient Autonomy
Informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical anesthesia practice, ensuring patients understand risks, benefits, and alternatives. It respects patient autonomy, allowing them to make decisions about their care.
Anesthesiologists must provide clear, unbiased information and ensure comprehension. This process is both a legal requirement and a commitment to patient-centered care, fostering trust and shared decision-making.
9.2 Legal Implications of Anesthesia Practice
Anesthesiologists must navigate legal responsibilities, including negligence claims and compliance with safety protocols. Proper documentation and adherence to guidelines are critical to avoid liability.
Understanding legal standards ensures patient safety and protects practitioners. Failure to meet these standards can result in legal consequences, emphasizing the importance of thorough practice and compliance.



